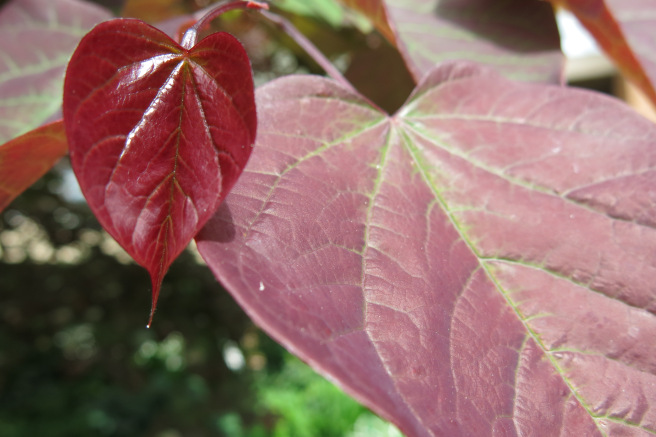
On the 27th of November 1835, a crowd of people gathered outside Newgate prison in the City of London to watch the first hanging there in two years.
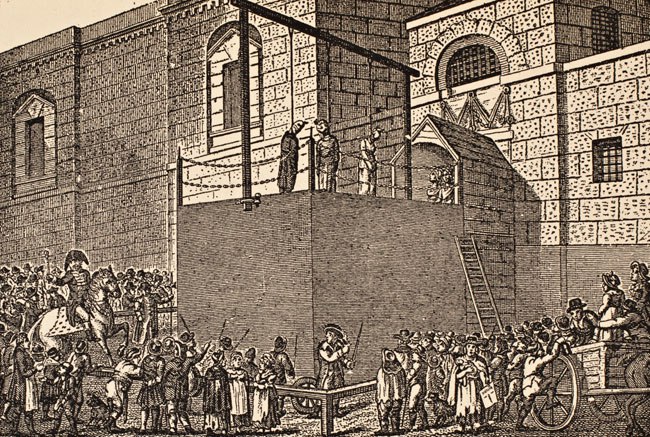

James Pratt (1805–1835) also known as John Pratt, and John Smith (1795–1835) were two London men who, in November 1835, became the last two to be executed for sodomy in England. Pratt and Smith were arrested in August of that year after being convicted of having sex in the room of another man, William Bonill.
“The grave will soon close over me,” Smith allegedly wrote to a friend before his hanging, “and my name [be] entirely forgotten.”
But that was not altogether true.
Unbeknownst to the sufferers, they were destined for literary preservation by a young writer on the make, one Charles Dickens:

Smith and Pratt make an appearance in Dickens’ Sketches by Boz, an 1836 compilation of London scenes of which “A Visit to Newgate” is perhaps the best-known.
The last Saturday of August 1835 was a beautiful hot day. James Pratt (30) left his wife and two young daughters in Deptford, searching for work – promising to return by 6pm. He was a labourer and needed a better job.
Pratt first visited his aunt in Holborn, before heading to Blackfriars. His aunt thought he’d had too much to drink and needed a rest, but he pressed on. In an ale house he met John Smith, a labourer aged 40, and William Bonill (sometimes spelled Bonell), aged 68. Neither could offer him a job to improve his financial situation but their company was hospitable. Bonill invited Pratt and Smith back to his rented flat and they accepted.
Little did they know as they made their way to his premises in nearby George Street, that this encounter would result in their execution – and that Bonill would be banished to the penal colony of Australia – all within a mere three months.

William Bonill, aged 68, had lived for 13 months in a rented room at a house near the Blackfriars Road, Southwark, London. His landlord later stated that Bonill had frequent male visitors, who generally came in pairs, and that his suspicions became aroused on the afternoon of 29 August 1835, when Pratt and Smith came to visit Bonill. The landlord climbed to an outside vantage point in the loft of a nearby stable building, where he could see through the window of Bonill’s room, before coming down to look into the room through the keyhole. Both the landlord and his wife later claimed they both looked through the keyhole and saw sexual intimacy between Pratt and Smith, so the landlord broke open the door to confront them. Bonill was absent, but returned a few minutes later with a jug of ale. The landlord went to fetch a policeman and all three men were arrested.
Pratt and Smith were charged with ‘buggery’ and Bonill as an accessory. They went on trial for their lives before Judge Baron Gurney at the Old Bailey on 21 September 1835.

William Bonill was convicted as an accessory and sentenced to 14 years of penal transportation. James Pratt was a groom,who lived with his wife and children at Deptford, London. A number of witnesses came forward to testify to his good character.
John Smith was from Southwark Christchurch and was described in court proceedings and newspaper reports as an unmarried labourer although other sources state he was married and worked as a servant. At the trial, no character witnesses came forward to testify on his behalf.
The conviction of the three men rested entirely on what the landlord and his wife claimed to have witnessed through the keyhole; there was no other evidence against them. One modern commentator has cast doubt on their testimony, based on the narrow field of vision afforded by a keyhole and the range of acts the couple claimed to have witnessed during the brief length of time they were looking.
The arresting police officer had no material evidence to support the charge. The account that Jane Berkshire told the jury is improbable. She said she watched for less minute but claimed to have witnessed the alleged sex acts, from the men undressing to laying on the floor and the “appearance” of anal penetration. She said she saw the men’s private parts but did not answer when asked whether either man had an erection. It seems doubtful that the keyhole could have provided the range of vision needed to see what she claimed.
The magistrate Hensleigh Wedgwood, who had committed the three men to trial,
 subsequently wrote to the Home Secretary, Lord John Russel, arguing for the commutation of the death sentences, stating:
subsequently wrote to the Home Secretary, Lord John Russel, arguing for the commutation of the death sentences, stating:
“It is the only crime where there is no injury done to any individual and in consequence it requires a very small expense to commit it in so private a manner and to take such precautions as shall render conviction impossible. It is also the only capital crime that is committed by rich men but owing to the circumstances I have mentioned they are never convicted.”
Wedgwood described the men as “degraded creatures” in another letter. Nevertheless, he argued that the law was unfair in their case as wealthy men who wished to have sex could easily afford a private space in which to do it with virtually no chance of discovery. Pratt and Smith were condemned only because they could only afford to use a room in a lodging house, in which they were easily spied upon.
On 5 November 1835, Charles Dickens and the newspaper editor John Black visited Newgate Prison; Dickens wrote an account of this in Sketches by Boz and described seeing Pratt and Smith while they were being held there.

“The other two men were at the upper end of the room. One of them, who was imperfectly seen in the dim light, had his back towards us, and was stooping over the fire, with his right arm on the mantel-piece, and his head sunk upon it. The other was leaning on the sill of the farthest window. The light fell full upon him, and communicated to his pale, haggard face, and disordered hair, an appearance which, at that distance, was ghastly. His cheek rested upon his hand; and, with his face a little raised, and his eyes wildly staring before him, he seemed to be unconsciously intent on counting the chinks in the opposite wall.”
— A Visit to NewgateThe jailer who was escorting Dickens confidently predicted to him that the two would be executed and was proven correct. Seventeen individuals were sentenced to death at the September and October sessions of the Central Criminal Court for offences that included burglary, robbery and attempted murder.
On 21 November, all were granted remission of their death sentences under the Royal Prerogative of Mercy with the exceptions of Pratt and Smith.This was despite an appeal for mercy submitted by the men’s wives that was heard by the Privy Council.

Pratt and Smith were hanged in front of Newgate Prison on the morning of 27 November. The crowd of spectators was described in a newspaper report as larger than usual;this was possibly because the hanging was the first to have taken place at Newgate in nearly two years. The event was sufficiently notable for a printed broadside to be published and sold.

This described the men’s trial and included the purported text of a final letter that was claimed to have been written by John Smith to a friend.
William Bonill was one of 290 prisoners transported to Australia on the ship Asia, which departed England on 5 November 1835 and arrived in Van Diemen’s Land (now Tasmania) on 21 February 1836.Bonill died at the New Norfolk Hospital in Van Diemen’s Land on 29 April 1841

Donation
I am passionate about my site and I know a you all like reading my blogs. I have been doing this at no cost and will continue to do so. All I ask is for a voluntary donation of $2 ,however if you are not in a position to do so I can fully understand, maybe next time then. Thanks
$2.00
Advertisements Share this: