A run level is a state of init and the whole system that defines what system services are operating. Services that get started at a certain run time are determined by the contents of the various rcN.d directories. Most distributions locate these directories either at /etc/init.d/rcN.d or /etc/rcN.d[N = run-level value]. There are six run-levels in Linux.
After the Linux kernel has booted, the init program reads the /etc/inittab file to determine the behaviour for each run level. If no specific run level is specified then Linux will continue to run in Default run level.
To check the default run-level in Linux kernel use command: runlevel 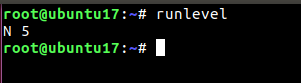
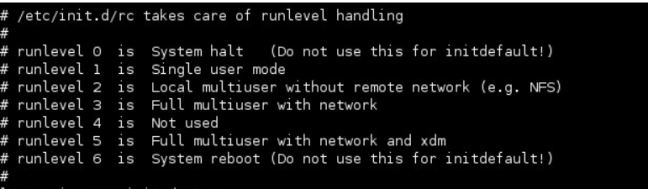
Linux Basic Run-levels:-
- LEVEL 0 —-> Shutdown —->Shut-down all services.
- LEVEL 1—–> Single user —->Used for system maintenance, it has no networking support.
- LEVEL 6—–>Reboot –>Shut-down all services and system the system is being rebooted.
Other Run-levels are:-
- LEVEL 2 —–>Multi-user mode without networking
- LEVEL 3——>Multi-user mode with networking
- LEVEL 5——> Multi-user mode with networking and GUI
While the system is running, the telinit command can change the run level. When the run level is changed, init runs the relevant command from /etc/inittab.
As sudo or su one can use “init 0″[poweroff] and “init 6″[reboot] the machine.
Advertisements Share this: